
Firewalls and virtual private networks (VPNs) stand as two crucial components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, safeguarding our online activities from unauthorized access, surveillance, and cyberattacks.
A firewall acts as a gatekeeper, filtering incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined rules. It sits between your device and the internet, scrutinizing each packet of data to ensure it aligns with established security policies. This protective barrier blocks malicious traffic, such as viruses, malware, and phishing attempts, preventing them from infiltrating your device or network.
In contrast, a VPN creates a secure tunnel between your device and a remote server, essentially creating a private network within the public internet. This encrypted connection hides your online activity from prying eyes, including your internet service provider (ISP), government agencies, and hackers. They are particularly useful for accessing blocked websites, protecting sensitive data when using public Wi-Fi, and maintaining anonymity while browsing the internet.
What is a Firewall?
A firewall is a network security device that acts as a barrier between your device or network and the internet. It controls the incoming and outgoing traffic, allowing or blocking data packets based on predetermined security rules. Firewalls help to protect your devices and network from unauthorized access, malicious attacks, and data breaches.
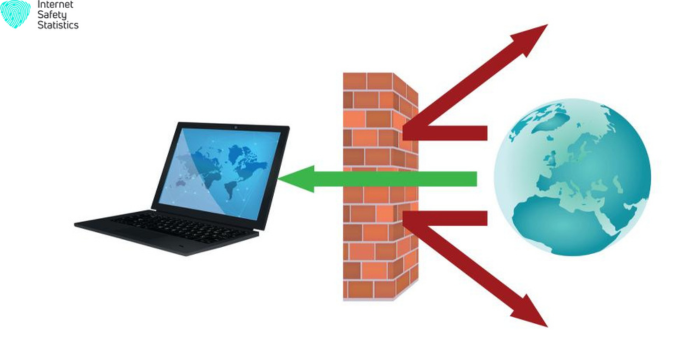
How firewalls work
- Packet filtering: Firewalls inspect the header of each data packet to determine its source and destination, port number, and other relevant information.
- Access control lists (ACLs): Based on predefined security policies, firewalls decide whether to allow or block the packet based on its characteristics and the established rules.
- Stateful inspection: Advanced firewalls maintain a state table that tracks the ongoing connections between devices, enabling more sophisticated traffic filtering and protection against advanced threats.
- Deep packet inspection (DPI): Some firewalls can analyze the actual contents of data packets, providing greater visibility and control over network traffic.
Functions of Firewalls in Network Security
- Protect against unauthorized access: Firewalls block unauthorized attempts to access your devices or network, preventing hackers from gaining control or stealing sensitive data.
- Mitigate cyberattacks: they help to prevent a wide range of cyberattacks, including malware, phishing, and denial-of-service attacks.
- Protect sensitive data: they safeguard confidential information, such as financial records, personal data, and intellectual property, from unauthorized exposure or theft.
Types of Firewalls and Network Traffic Filtering
Firewalls can be broadly categorized into three main types:
- Packet-filtering firewalls: These firewalls examine the headers of data packets to determine their source and destination, port number, and other relevant information. Based on predefined security policies, packets are allowed or blocked based on these characteristics.
- Stateful inspection firewalls: These firewalls maintain a state table that tracks the ongoing connections between devices. They consider the context of the traffic, such as the established connection, to make more informed decisions about packet filtering.
- Application-level firewalls (proxy servers): These firewalls examine the content of data packets, providing greater visibility and control over network traffic. They can filter based on the type of application, user authentication, and other criteria.
How Firewalls Filter Network Traffic
Firewalls employ various methods to filter network traffic:
- Access control lists (ACLs): These are lists of rules that define which types of traffic are allowed or blocked. ACLs can be based on source IP address, destination IP address, port number, protocol, and other factors.
- Security groups: Security groups are collections of ACLs that can be applied to specific network devices or groups of devices. This simplifies the management of firewall rules and provides a more granular approach to network security.
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS): IDSs monitor network traffic and identify suspicious activity, while IPSs can actively block or mitigate malicious attacks.
By combining these filtering methods, firewalls effectively protect networks from a wide range of threats.
What is a VPN?
A virtual private network (VPN) is a secure connection that creates a private network over a public network, such as the Internet. VPNs encrypt your internet traffic, masking your IP address and protecting your online activity from prying eyes. By connecting to a VPN, you can access your company’s network securely while working remotely, browse the internet without being tracked, and bypass geo-restrictions that may block certain websites or content.

How VPNs Work?
- Establishing a VPN tunnel: When you connect to a VPN, your device establishes a secure connection with a VPN server.
- Encryption: All data transmitted between your device and the VPN server is encrypted, making it unreadable to anyone who intercepts it.
- Masquerading IP address: The VPN server assigns your device a temporary IP address from its pool, concealing your true IP address and location.
Types of VPNs
There are three main types of VPNs:
- Site-to-site VPNs: They connect two private networks, such as a company’s headquarters and its branch offices. They allow employees at different locations to securely access the company’s network resources.
- Remote access VPNs: These allow remote users to connect to a private network from a public location, such as a coffee shop or airport. They are typically used by employees who work from home or on the go.
- Mobile VPNs: They are a type of remote access VPN that is specifically designed for mobile devices. They can be used to connect smartphones, tablets, and laptops to a private network, even when the devices are not connected to a Wi-Fi network.
Benefits of Using a VPN
There are many benefits to using a VPN, including:
- Protecting data privacy: they encrypt your internet traffic, making it unreadable to anyone who intercepts it, including your internet service provider (ISP), hackers, and government agencies. This can help to protect your privacy and prevent your data from being tracked or stolen.
- Accessing corporate resources remotely: they allow you to connect to your company’s network securely from anywhere in the world. This can be essential for employees who work remotely or on the go.
- Bypassing Internet censorship: they can be used to bypass Internet censorship, allowing you to access websites and content that may be blocked in your region. This can be important for people who live in countries with authoritarian governments or restrictive internet policies.
- Secure public Wi-Fi: Using a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi can help protect your data from hackers who may be lurking on the network.
- Online anonymity: they can mask your IP address, making it difficult for websites to track your online activity. This can help to protect your online anonymity and prevent targeted advertising.
Overall, VPNs are a valuable tool for protecting your privacy and security online. They can be used for a variety of purposes, including accessing corporate resources remotely, bypassing internet censorship, and securing public Wi-Fi connections.
Firewall and VPNs: Comparison of Network Security and Privacy for
Firewall
- Network Security: Focuses on protecting the network from unauthorized access, malicious attacks, and data breaches.
- Privacy: Protects network traffic from unauthorized inspection, but does not encrypt traffic, so data can still be visible to the ISP.
VPN
- Privacy: Encrypts traffic, masking IP addresses and protecting online activity from prying eyes.
- Network Security: This does not directly protect the network from unauthorized access or attacks, but can help protect personal data from being intercepted when using public Wi-Fi.
Conclusion
They are both essential tools for protecting network security and privacy. Firewalls act as a first line of defense against unauthorized access and attacks, while VPNs safeguard online privacy and security, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks. By implementing both of them, you can create a robust cybersecurity posture that protects your devices, network, and online activities from a wide range of threats.
Choosing Between a Firewall and a VPN
Choosing between firewall and VPN depends on several factors, including network size and complexity, security requirements, cost, and user needs.
Network size and complexity
- Small networks: For small networks with one or two computers, a firewall may be sufficient. However, as networks grow larger and more complex, firewalls may not be able to provide adequate protection. In these cases, a VPN may be a better option.
- Large networks: For large networks with multiple devices and users, a firewall and a VPN are often used together. The firewall provides perimeter security, while the VPN provides secure remote access and protection of sensitive data.
Security requirements
- Protecting against known threats: Firewalls are good at blocking known threats, such as malware and viruses. However, they may not be able to protect against new or unknown threats. VPNs, on the other hand, use encryption to protect all data that passes through the VPN tunnel, regardless of whether it is known to be malicious.
- Protecting against data breaches: Firewalls can help prevent unauthorized access to networks, but they cannot protect against data breaches that occur once attackers have gained access. VPNs can help to protect against data breaches by encrypting data and masking IP addresses.
- Meeting compliance requirements: Some organizations have specific security requirements that they must meet. For example, healthcare organizations must comply with HIPAA regulations, which require them to protect patient data. In these cases, a VPN may be necessary to meet compliance requirements.
Cost
- Firewalls: Firewalls can be purchased as hardware devices or as software. Hardware firewalls are typically more expensive than software firewalls, but they can provide more robust security.
- VPNs: VPNs can be purchased from a service provider or installed on your device. Paid VPN services typically offer more features and support than free VPN services. However, free VPN services may not be as secure, some of the most popular VPN services are CyberGhost, NordVPN, and Surfshark.
User needs
- Remote access: If you need to access your network remotely, a VPN is essential. Firewalls typically do not provide remote access capabilities.
- Privacy: If you are concerned about your online privacy, a VPN can help to protect your data from being tracked by third parties.
- Geo-restrictions: If you need to access websites or content that is blocked in your region, a VPN can help you to bypass those restrictions.
In general, firewalls are a good choice for protecting small networks from known threats. VPNs are a good choice for larger networks, remote access, and protecting sensitive data.
Which is Beneficial for Network Security?
Choosing between a firewall and a VPN depends on your specific needs and security requirements, the following scenarios are presented:
Scenarios Where Firewalls are Beneficial for Network Security
- Protecting against unauthorized access: Firewalls act as a gatekeeper, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined security rules. This prevents unauthorized users, such as hackers, from gaining access to your network and potentially stealing sensitive data or disrupting operations.
- Mitigating cyberattacks: they can help to prevent a wide range of cyberattacks, including malware, phishing, and denial-of-service attacks. By blocking malicious traffic, firewalls can safeguard your network and its devices from these threats.
- Protecting sensitive data: Firewalls can help to protect confidential information, such as financial records, personal data, and intellectual property, from unauthorized access or theft. By filtering traffic based on access permissions and data sensitivity, firewalls can ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive information.
- Enhancing network perimeter security: Firewalls can be deployed at network gateways to create a secure perimeter, separating the internal network from the public internet. This helps to prevent unauthorized access from the outside world and restricts network traffic to only authorized sources.
Scenarios where VPNs are Crucial for Secure Remote Access
- Accessing corporate resources remotely: VPNs allow employees to securely connect to their company’s network from any location, including their homes, coffee shops, or even while traveling. This enables remote workers to access company files, applications, and other resources as if they were physically present in the office.
- Securing public Wi-Fi connections: Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making them vulnerable to eavesdropping and data theft. By using a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi, users can encrypt their internet traffic and mask their IP address, protecting their privacy and security.
- Bypassing Internet censorship: In some countries, the Internet is censored, restricting access to certain websites or content. VPNs can be used to bypass these restrictions by routing traffic through a secure server in a different location. This allows users to access information and resources that may be blocked in their region.
- Maintaining online anonymity: they can mask a user’s IP address, making it difficult for websites or third parties to track their online activity. This can help to protect users’ privacy and prevent them from being targeted with personalized advertising or surveillance.
- Accessing geo-restricted content: Some streaming services, websites, or other online resources may be restricted to specific regions due to licensing or copyright agreements. they can be used to bypass these geo-restrictions by connecting to a VPN server in a different location. This allows users to access content that may be blocked in their home region.
In conclusion, Both play complementary roles in protecting network security and user privacy. Firewalls act as a first line of defense, filtering incoming and outgoing traffic to prevent unauthorized access and malicious attacks. VPNs, on the other hand, provide secure remote access, protect sensitive data while using public Wi-Fi, and allow users to bypass internet censorship and geo-restrictions. By implementing both firewalls and VPNs, individuals and organizations can create a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy that safeguards their networks, devices, and online activities.
