
If you’ve been a victim of cyber attacks on the internet, you might have heard about phishing and pharming attacks!
These two cyber threats might sound similar, but they’re actually quite different beasts lurking in the digital depths. So, in order to avoid these attacks, you have to understand both and the difference between them.
What is Phishing?
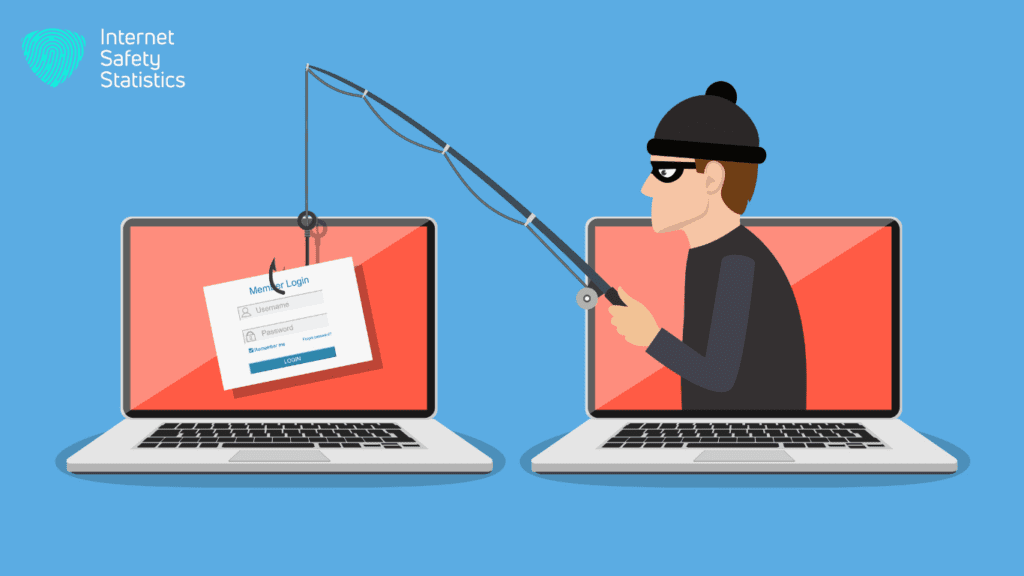

Phishing is a fraudulent attempt to steal your personal information, such as your login credentials, credit card details, or other sensitive data. It’s like a cybercriminal casting a line with a tempting lure, hoping you’ll take the bait and reveal your valuable information.
Imagine a fake bank email that threatens to suspend your account unless you click on a suspicious link and update your details. Or perhaps a text message from a delivery company claiming your package is being held and you need to pay a fee to release it. These are just two examples of phishing scams.
Phishing attacks can be very convincing, often using logos, colours, and language that mimic legitimate companies or organisations. This makes it even more important to be aware of the dangers and how to protect yourself.
Phishing Attack Defined
A phishing attack is a multi-step process designed to trick you into compromising your security. Here’s how it typically works:
- The Bait: The attacker sends you a message, usually via email, text message, or social media, that appears to be from a trusted source.
- The Hook: The message creates a sense of urgency or fear, prompting you to take immediate action. This could be a threat of account suspension, a promise of a reward, or a warning about a fake security breach.
- The Reel: The message includes a call to action, such as clicking on a link, downloading an attachment, or providing your personal information.
- The Catch: If you take the bait, you’ll be directed to a fake website, or malware will be installed on your device. The attacker can then steal your login credentials, financial information, or other sensitive data.
Common Phishing Scams
Phishing scams come in many forms, but some of the most common include:
- Email phishing: This is the most common type of phishing attack, where you receive an email that appears to be from a legitimate company or organisation.
- Smishing: This is similar to email phishing, but the attack is carried out via SMS text messages.
- Vishing: This involves phishing attacks conducted over the phone.
- Whaling: This is a targeted phishing attack aimed at high-profile individuals, such as CEOs or celebrities.
- Spear phishing: This is a type of phishing attack that targets specific individuals or groups of people.
How Phishing Works
Phishing attacks rely on a combination of social engineering and technical tricks to deceive victims. Here are some of the common tactics used:
- Spoofing: This involves making the sender’s name and email address appear to be from a legitimate source.
- Urgency and Scarcity: Phishing messages often create a sense of urgency or scarcity to pressure you into taking action without thinking.
- Threats and intimidation: Some phishing messages may threaten you with negative consequences if you don’t take action.
- Typos and grammatical errors: While not always present, some phishing messages may contain typos or grammatical errors to make them appear more legitimate.
Types of Phishing
There are many different types of phishing attacks, but some of the most common include:
- Clone phishing: This involves sending emails that are almost identical to legitimate emails from a trusted source.
- Deceptive phishing: This involves sending emails that are designed to deceive the recipient into thinking they are from a legitimate source.
- Pretexting phishing: This involves creating a fake scenario to trick the recipient into revealing their personal information.
- Quid pro quo phishing: This involves offering something of value in exchange for personal information.
Preventing Phishing Attacks
You can protect yourself from phishing attacks by following these tips:
- Be suspicious of unsolicited emails, text messages, and phone calls. Even if they appear to be from a trusted source, don’t click on any links or attachments unless you’re sure they’re legitimate.
- Hover over links to see the real destination URL before clicking.
- Never enter your personal information in response to an unsolicited email, text message, or phone call.
- Be wary of emails with typos or grammatical errors.
- Keep your software up to date, including your antivirus and web browser.
- Use strong passwords, and don’t reuse them for multiple accounts.
- Report phishing attacks to the sender’s email provider or social media platform.
What is Pharming?

While phishing casts a wide net, pharming takes a more targeted approach, manipulating the internet’s infrastructure itself to trick you into landing on a fake website. Let’s delve deeper into this devious tactic:
Pharming Attack Explained
Pharming is a cyberattack that redirects your web traffic to a malicious website, often mimicking a legitimate one. Imagine you type “yourbank.com” into your browser, but due to pharming, you end up on a fake bank website designed to steal your login credentials. This can happen in two main ways:
- DNS poisoning: Attackers manipulate the Domain Name System (DNS), which translates domain names like “yourbank.com” into IP addresses. By injecting fake entries, they can redirect you to the wrong website.
- Host file manipulation: The host file on your computer maps domain names to IP addresses. Attackers can modify this file to point you to a fake website.
How Pharming Scams Work
Pharming scams often involve these steps:
- Target selection: Attackers choose websites with valuable information, like online banking or e-commerce platforms.
- Infrastructure manipulation: They use DNS poisoning or host file manipulation to redirect traffic to a fake website.
- Website spoofing: The fake website mimics the look and feel of the legitimate one, making it difficult to distinguish.
- Data theft: Once you enter your information on the fake website, attackers steal it for their malicious purposes.
Securing Against Pharming Attacks
Here are some ways to protect yourself from pharming:
- Use HTTPS: Look for the padlock symbol and “https” in the address bar to ensure a secure connection.
- Keep software updated: Update your operating system, web browser, and antivirus software regularly.
- Be cautious of suspicious links: Don’t click on links in emails, text messages, or social media posts unless you’re sure they’re legitimate.
- Use a VPN: A VPN encrypts your internet traffic, making it harder for attackers to intercept it.
- Be wary of public Wi-Fi: Avoid entering sensitive information on public Wi-Fi networks.
Impact of Pharming on Security
Pharming poses a significant threat to online security, as it can bypass traditional security measures like firewalls and antivirus software. It can lead to:
- Identity theft: Attackers can use your stolen information to access your bank accounts, credit cards, and other online accounts.
- Financial loss: You may lose money through unauthorised transactions or scams.
- Data breaches: Pharming can be used to launch larger attacks, such as data breaches, that affect entire organisations.
The Deceptive Duo: Phishing And Pharming

Both phishing and pharming aim to steal your sensitive information online, but they operate in distinct ways. Let’s untangle the web of deceit and unveil the key differences between these cyber threats.
How Do Phishing and Pharming Differ?
Picture the internet as a bustling marketplace. Both phishing and pharming lurk like cunning pickpockets, seeking to snatch your valuable data. The key difference? Their tactics:
Phishing: Imagine the pickpocket slipping you a fake wallet that looks real. You click a deceptive link, enter your information, and bam! Stolen.
Pharming: Here, the pickpocket tampers with the market stalls themselves. You innocently walk up to the “bank,” hand over your details, and bam! Stolen without even realising the stall was a sham.
In essence:
- Phishing relies on tricking you into visiting fake websites.
- Pharming manipulates the internet infrastructure to send you there automatically.
Both phishing and pharming are dangerous, but recognising their distinct approaches is the first step towards digital self-defence. So, stay vigilant, stay informed, and remember: in the online marketplace, trust only the familiar stalls, and double-check before handing over your digital wares.
| Feature | Phishing | Pharming |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Individual users | Any user accessing the targeted website |
| Attack Method | Deceptive messages to trick users | Manipulation of DNS to redirect traffic |
| User Control | Users can be cautious about suspicious messages | Users have little control if DNS is compromised |
| Technical Skill | Requires higher technical skills and access to DNS systems | Requires higher technical skill and access to DNS systems |
| Prevention | Lower technical skills required | Keeping software updated, using secure connections, DNS security services |
Cyber Risks in Phishing and Pharming
Both phishing and pharming pose serious threats, but understanding their differences allows for more effective prevention strategies. Staying vigilant, practising good online hygiene, and employing appropriate security measures are essential to navigating the digital landscape safely.
| Risk | Phishing | Pharming |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Difficulty | Easier to detect suspicious emails and websites | Harder to detect, as the fake website appears legitimate |
| Potential Impact | Individual data theft | Widespread data breaches affecting many users |
| Prevention Focus | User awareness and vigilance | Technical measures like DNS security and software updates |
Preventive Measures for Phishing and Pharming
Phishing and pharming might lurk in the shadows of the digital world, but your defence doesn’t have to stay in the dark. Here’s a comprehensive arsenal of preventive measures to shield yourself from these deceptive attacks:
Enhancing Cybersecurity Against Phishing and Pharming
- Multi-layered Defense: Employ a combination of strategies like antivirus software, firewalls, DNS security, and website authentication tools to create a robust defence.
- Software Updates: Update your operating system, web browser, and antivirus software regularly to patch vulnerabilities exploited by phishers and pharmers.
- Secure Connections: Look for the padlock symbol and “https” in the address bar to ensure a secure connection before submitting any sensitive information.
Protecting Personal Information from Phishing and Pharming
- Think Before You Click: Never click on suspicious links or open attachments in emails, texts, or social media messages, even if they appear to be from legitimate sources.
- Hover to Reveal: Hover over links to see the actual destination URL before clicking to verify its legitimacy.
- Double-check URLs: Manually type trusted website addresses instead of clicking on links to avoid being redirected by pharming.
- Strong Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for all online accounts and enable two-factor authentication for added security.
Implementing DNS Security to Counter Phishing and Pharming
- DNS Encryption: Opt for DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH) or DNS-over-TLS (DoT) to encrypt your DNS queries, preventing attackers from tampering with them.
- DNS Filtering: Utilise DNS filtering services to block access to known phishing and pharming websites.
Awareness Training for Phishing and Pharming Prevention
- Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the latest phishing and pharming techniques to recognise the red flags.
- Train Your Team: Implement regular cybersecurity awareness training for employees and family members to equip them with essential knowledge and skills to identify and avoid these threats.
Using Antivirus Solutions for Defending Against Phishing and Pharming
- Advanced Antivirus: Choose an antivirus solution with phishing and pharming detection capabilities to proactively block malicious websites and emails.
- Real-time Protection: Ensure your antivirus is updated with the latest definitions and runs in real-time for continuous protection.
Remember: Both phishing and pharming pose serious threats to your online security. Stay informed, practice scepticism, and employ protective measures to navigate the digital world safely.
